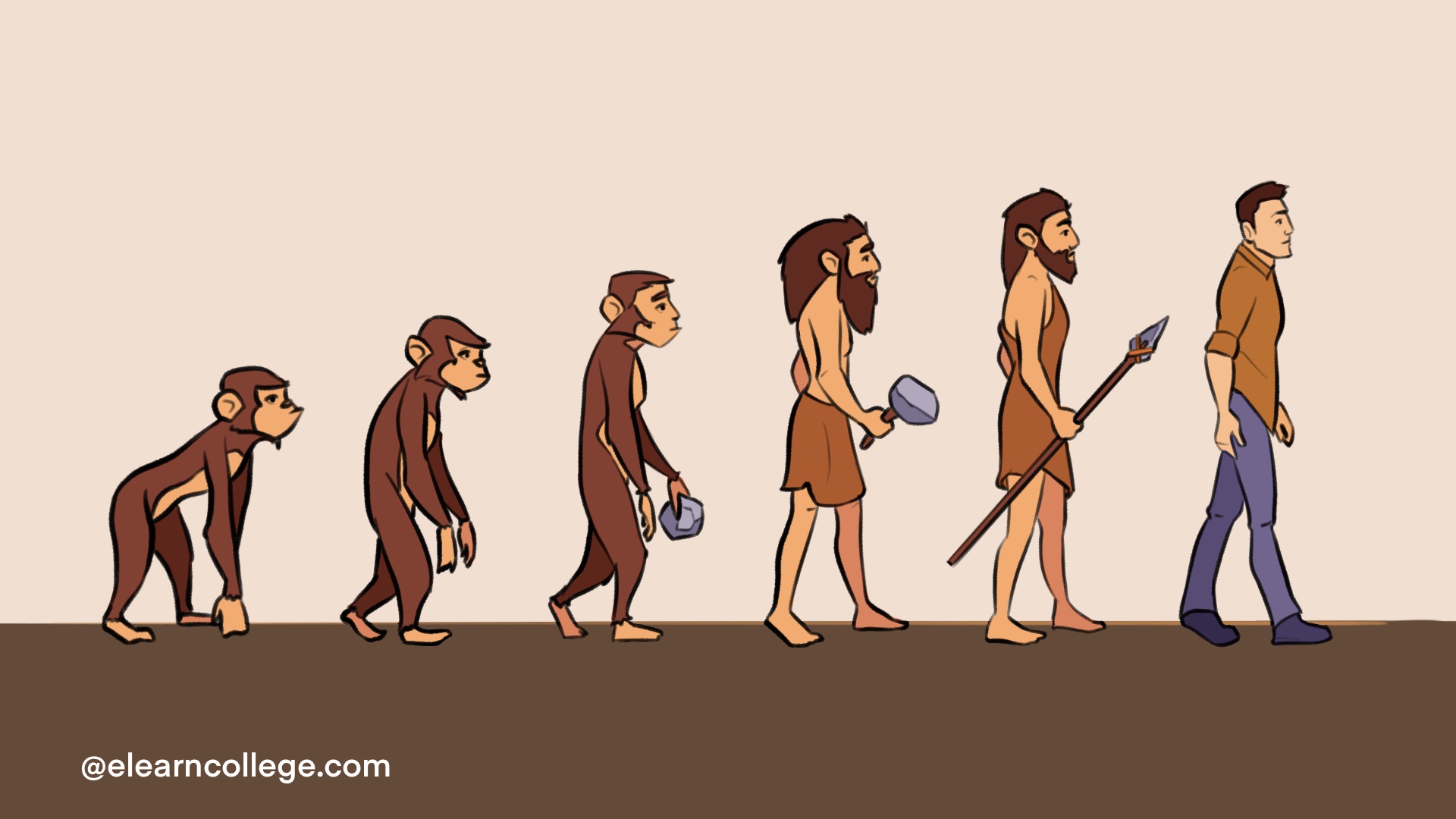
The journey from monkey to human evolution is one of the most fascinating narratives in the history of our species. It encapsulates an extraordinary tale of adaptation, survival, and transformation that spans millions of years. As we delve into this intricate history, we uncover the connections that bind us to our primate relatives and the evolutionary milestones that have shaped who we are today. Exploring this journey not only enriches our understanding of human biology but also highlights the remarkable traits that characterize us as a species.
Our story begins in the lush forests of ancient Earth, where the first primates emerged around 65 million years ago. These creatures, small and arboreal, navigated their environments with agility and intelligence. Over time, these early ancestors branched out into various species, including the lineage that would eventually lead to modern humans. This evolutionary path is marked by significant adaptations that enabled our forebears to thrive in diverse habitats, giving rise to the incredible biological and cultural diversity we see in humans today.
As we embark on this exploration of monkey to human evolution, we will address fundamental questions about our origins, the traits we share with primates, and the milestones that have defined our development. By examining fossil records, genetic evidence, and behavioral studies, we can piece together the puzzle of our past and gain insight into the evolutionary forces that have shaped humanity.
What Are the Key Stages in Monkey to Human Evolution?
The evolution from monkey to human is not a straight line but rather a complex web of branching paths. Here are the key stages:
- Early Primates (65 Million Years Ago): The emergence of the first primates set the stage for future evolution.
- Prosimians (55 Million Years Ago): These include lemurs and tarsiers, marking an important evolutionary step.
- Monkeys (40 Million Years Ago): The divergence of Old World and New World monkeys occurred during this period.
- Apes (25 Million Years Ago): The evolution of apes introduced larger brains and more complex social structures.
- Hominids (6-7 Million Years Ago): The lineage that would lead to humans split from that of chimpanzees.
- Australopithecines (4 Million Years Ago): Early bipedal hominids that exhibited both ape-like and human-like traits.
- Genus Homo (2.5 Million Years Ago): The emergence of our genus marked significant advancements in tool use and culture.
- Modern Humans (200,000 Years Ago): Anatomically modern humans appeared, leading to the development of civilizations.
How Did Environmental Changes Influence Human Evolution?
Environmental changes played a crucial role in shaping the evolutionary journey from monkey to human. As climates shifted, forests transformed into savannahs, forcing our ancestors to adapt in several ways:
- Bipedalism: Walking on two legs freed the hands for tool use and carrying objects.
- Dietary Changes: A shift from fruit-based diets to a more diverse range of foods, including meat.
- Social Structures: Larger groups became necessary for survival, leading to complex social interactions.
- Cognitive Development: As challenges increased, so did the need for advanced problem-solving skills.
What Genetic Evidence Supports the Monkey to Human Evolution Theory?
Genetic studies have provided compelling evidence for the evolutionary link between monkeys and humans. Here are some key findings:
- Shared DNA: Humans share approximately 98.8% of their DNA with chimpanzees, our closest living relatives.
- Genetic Markers: Specific genes associated with brain development and function show similarities across primate species.
- Evolutionary Clocks: Molecular clocks help estimate when species diverged based on genetic mutations.
How Does Fossil Evidence Illuminate Our Understanding of Evolution?
The fossil record serves as a crucial tool in understanding the monkey to human evolution. Key fossil discoveries include:
- Australopithecus afarensis: "Lucy," a famous fossil, showcases early bipedalism.
- Homo habilis: Considered one of the first members of our genus, known for tool use.
- Neanderthals: Close relatives that provide insight into human adaptation and culture.
What Role Did Culture Play in Human Evolution?
Cultural evolution has significantly influenced the monkey to human evolution process. Some aspects include:
- Language Development: The emergence of complex language allowed for advanced communication and social organization.
- Tool Use: The development of tools enabled our ancestors to manipulate their environment effectively.
- Art and Symbolism: The creation of art reflects cognitive complexity and cultural expression.
How Are Humans Different from Monkeys Today?
Despite our common ancestry, modern humans exhibit numerous differences from monkeys:
- Brain Size: Humans have larger brains relative to body size, leading to advanced cognitive abilities.
- Bipedalism: Humans walk upright on two legs, while monkeys primarily use all fours.
- Social Structures: Human societies are more complex, with intricate cultural norms and values.
Conclusion: What Lies Ahead in Our Understanding of Monkey to Human Evolution?
As science continues to evolve, so too does our understanding of monkey to human evolution. Ongoing research in genetics, anthropology, and archaeology promises to shed further light on our origins and the intricate tapestry of life that connects us to our primate relatives. In exploring our past, we not only learn about where we came from but also gain insights into the future of humanity and our role in the natural world.
Embrace The Day: Kelly's Treehouse Good Morning Quotes
Adam Pearson: A Journey Of Resilience And Inspiration
Exploring The Baltimore City Schools Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide